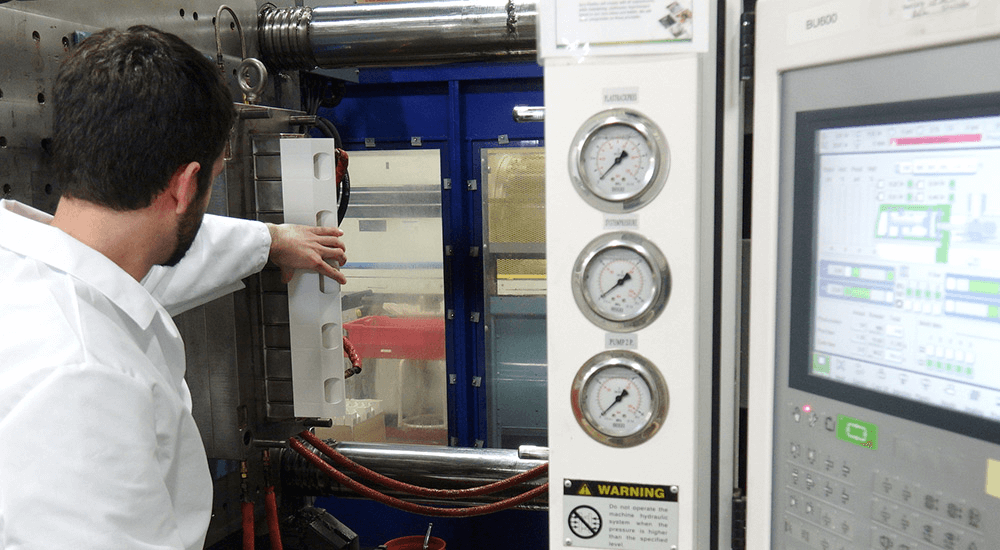
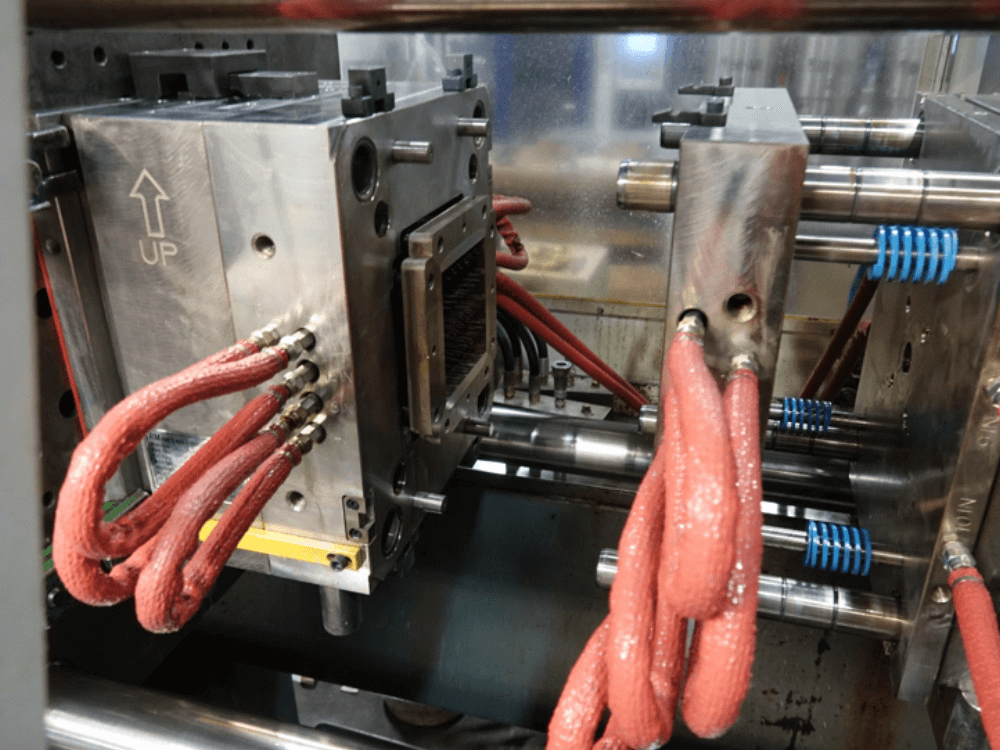
The Advantages of Injection Molding
Manufacturers typically turn to the plastic injection molding process to produce a large volume of a particular part, for several main reasons:
Consistent & Repeatable
The molds used for injection molding offer one of the strongest guarantees that parts will match the original. This lends to brand-consistent quality and part reliability and reduces the amount of plastic material waste.
Injection molded products are also incredibly durable and resistant to wear and tear.
Easily Scalable Production
Injection molding is a perfect solution for scaling large volume or mass production due to the simplicity and consistency of the process. Standardized injection molds allow manufacturers to dial in the specific requirements of their product and reproduce them quickly and accurately.
Low Price Per Unit
After setup costs are paid off, the price per unit of products manufactured via injection modeling drops steeply and remains extremely low. The more parts produced, the lower the individual cost, making plastic injection molding especially suitable for high volume production.
What Plastics & Resins Are Used in Injection Molding?
Aero-Plastics has the ability to mold nearly all engineered resigns, including:
- Polypropylene
- Polyethylene
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
- Polycarbonates
- Nylon
- PEEK
- Ultem
Depending on your application, certain materials may be more suitable than others. For example, if you need a high-strength but flexible material to fill your mold tool, thermoplastic materials like ABS might be best. High-density polyethylene, on the other hand, features a high chemical resistance, making it suitable for products or components that will be exposed to moisture or chemicals.
Our knowledgeable team can help you determine the best plastic materials and process for your specific application and unique needs.
Contact Us for More Information
Important Factors to Consider for Injection Molding
Injection molded products may be better suited for some projects over others, and understanding more about the plastic injection molding process can help you make an informed decision.
Before deciding on injection molding for your manufacturing process, it’s essential to consider a few key factors, including:
Quantity
Before selecting plastic injection molding as your production method, it’s important to first determine how many parts need to be produced in order to make the process (and initial investment) cost-effective. You may do this by figuring out how many parts it will take to break even on the project, and building in a conservative margin.
Budget
Injection mold production requires a significant up-front cost, in order to prepare the mold and manufacturing setup. However, this subsequently ensures a low production cost after that initial investment is paid off.
Part and Tool Design
If a part is to be produced by injection molding, this must be considered in its design — this includes simplifying its geometry and number of components as much as possible. The mold should be designed with a goal of minimizing the risk of defects during the production process.
Designs that are well-suited for plastic injection molding should ideally have a uniform wall thickness, as well as avoid sharp corners, undercuts, and other features that could increase manufacturing time or, in some cases, require additional molding processes for an individual injection molded part.
Production
For injection molding, it’s prudent to minimize cycle time as much as possible. The more time you can cut from the cycle, the more money you’ll save.
Simplifying production times often comes down to finding ways that can reduce the number of steps or tooling changes during the injection molding process. This could involve combining parts into a single section or reducing gate locations on the product.
It also helps to keep assembly simple – the more parts required in the setup, the higher the cost, so it’s often beneficial to keep injection molded parts as self-contained as possible.
Aero-Plastics’ Injection Molding Tolerance Objectives
Injection molding tolerances, listed below, are directly related to the material to be molded; part size and part geometry. We review parts and tolerances on a case-by-case basis during quoting, and use a Design for Manufacture process to align your project goal to our manufacturing methods.
We want you to achieve the best value possible — so our experts work with you on these tolerance objectives. Over-specified tolerances can increase project costs, and we understand how to minimize them without sacrificing product quality.
At Aero-Plastics, we strive to provide the highest quality plastic injection molding with the following tolerance objectives, which relate directly to the material to be molded.
Assess All Factors That Influence Applicable Tolerances
Our team of experts will assess physical factors that can influence tolerances, namely the material being used as well as the size and shape of the part being manufactured.
Material
The molding material affects all applicable tolerance objectives, from shrinkage rate to physical properties and cost.
Part Size
Larger parts require a larger tool set and will have greater variation in wall thickness, which can often create an increase in available
tolerances.
Part Geometry
The more complex a part’s geometry is, the higher the tolerance objective has to be in order to maintain quality and consistency. Complex features with tight tolerances may require substantial design revisions or additional tooling.
Review All Injection Molded Quotes
Our team is sure to review parts and tolerances on a case-by-case basis for all plastic injection molding quotes to ensure that we can deliver on all objections and achieve optimal part quality.
Follow Our Design for Manufacture Process
We use a Design for Manufacture process to align your project goal to our manufacturing methods. This process allows us to evaluate the design of a part and molding process before production begins – which ensures that we can successfully meet your requirements and attain part quality.
Provide Post-Molding Machining Processes As Needed
For tight tolerance parts, we can combine molding with post-mold machining operations. We’re on the Boeing QPL for all types and classes of molded parts, and an approved molder on the D14426 for BAC 5321 class II injection molded parts.
Manufactured Parts Suited for the Injection Molding Process
Aero-Plastics offers injection molding services for a variety of applications including medical, consumer goods, industrial equipment, automotive components and more. We have the capabilities to provide you with a custom solution that meets your needs.
Products that are well-suited for injection molding include:
- Medical Devices (like syringes, surgical devices, or implant parts)
- Home Appliances
- Automotive Parts
- Circuit Boards
- Ejector Pins
- Toys (like plastic bricks)
- Bottle Caps
- Air Vents
Unsure if your part is suited for the injection molding process? Our experienced engineers are happy to answer any questions you have and will work with you to determine if plastic injection molding is right for your project.
Contact Us for a Quote
Our molding tolerance objectives:
- The material used dictates the tolerances that can be maintained.
- Size and part geometry influence the tolerances.
- Aero-Plastics reviews all injection molded quotes to ensure the part quality and objectives can be delivered.
- Aero-Plastics uses a Design for Manufacture process to attain part quality.
- In cases of very tight tolerances, we can use post-molding machining processes.